苏州微流纳米生物技术有限公司
Nanoliposomesprepared from phospholipids and appropriate surfactants have sufficient flexibility. When used as a transdermal drug delivery carrier for hydrophilic proteins, this type of liposome can be deformed and "squeezed" into the stratum corneum under the influence of the osmotic pressure generated by the hydration of the stratum corneum, thus significantly increasing the transdermal penetration of the drug.
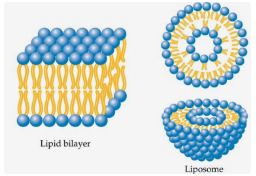
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of
liposomes Cyclosporine has strong lipophilicity, high molecular weight (molecular weight is 1202) and a circular structure. Transdermal transport is very difficult. Even if it is transported to the dermis to treat psoriasis, satisfactory results have not been achieved. In order to promote the percutaneous penetration of cyclosporine, the preparation method and physical and chemical properties of cyclosporine flexible nanoliposomes were studied.

Figure 2 On the front page of the article,
quantitatively weigh phosphatidylcholine, sodium cholate (the total amount of phosphatidylcholine and sodium cholate is 7.5%) and cyclosporine (37.5mg), add 30ml of chloroform-methanol (1:1) composite solvent, and remove the organic solvent by rotary evaporation in a constant temperature water bath at 37 degrees Celsius to form film materials such as phospholipids. Form a uniform lipid film on the wall of the flask. Then 10ml of 0.9% NaCl hydration medium was added to the round-bottom flask, and the membrane was rotated and washed for 2 hours to obtain a flexible liposome suspension. Prepare ordinary liposome suspensions without sodium cholate in the formulation at the same ratio.
The liposome suspension is subjected to probe ultrasound under ice water bath conditions for an appropriate time to obtain a nanoliposome colloidal solution, which is placed at room temperature, and filtered through a 0.15μm microporous filter membrane to remove titanium particles and other impurities released by the probe.
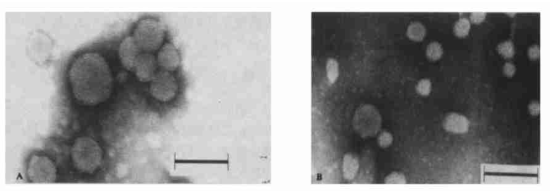
Figure 3 Observation results of flexible nanoliposomes (A) and ordinary nanoliposomes (B) under transmission electron microscope.
There is no obvious difference in appearance between flexible nanoliposomes and ordinary nanoliposomes under electron microscope. The average particle size of flexible nanoliposomes is 74.0 nm and the polydispersity index is 0.146; the average particle size of ordinary nanoliposomes is 61.8 nm and the polydispersity index is 0.506. Although the particle size of flexible nanoliposomes is larger than that of ordinary nanoliposomes, the polydispersity index is smaller, indicating that due to the addition of sodium cholate, the large particles have greater deformation and are easy to rupture, and the particle size distribution becomes uniform, thus forming nearly monodisperse particles.
Jin241213M