苏州微流纳米生物技术有限公司
Amikacin (AMK) is a semi-synthetic derivative of kanamycin-A with a special structure that is protected from damage by aminoglycoside inactivating enzymes, and therefore has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against gram-negative bacteria and many strains resistant to other aminoglycosides. Its mechanism of action is to inhibit the synthesis of bacterial proteins by closely binding to the A site in the 16S rRNA decoding region of the 30S subunit of the bacterial intracellular ribosome. It can also change the permeability of the bacterial cell wall, causing intracellular salts and nutrients to leak out, causing the bacteria to die quickly. Prolonging the action time of AMK, reducing the dosage, and reducing toxic and side effects are the direction of research and development of new preparations of aminoglycosides.
Multivesicular liposomes (MVLs) are foam spherical aggregates packed tightly with a large number of aqueous vesicular chambers inside. Therefore, as an excellent carrier for water-soluble drugs, it has high encapsulation efficiency and can effectively extend the half-life of the drug, reduce the dosage, and reduce toxic and side effects.
In this study, AMK was used as a model drug, natural phospholipids were selected as film-forming materials, and stearylamine and polyvinyl alcohol were used as membrane stabilizers to further prepare AMK-MVLs suspension.

Figure 1
Weigh the prescription amount of soybean phospholipids, cholesterol, triolein, and stearylamine on the front page of the article (Soybean phospholipid: cholesterol =1.91:1, glycerol trioleate amount is 1.02%), add 3 mL of chloroform, heat and dissolve in a constant temperature water bath of 37 - 40 degrees Celsius, as the oil phase; dissolve AMK in an equal volume of 7% sucrose aqueous solution, as the internal water phase; use a syringe to absorb the internal water phase and slowly inject it into the continuously stirred oil phase. In an ice-water bath, the probe is ultrasonically emulsified and dispersed to form stable W/O type colostrum; Use a syringe with a thin needle to aspirate 1 mL of colostrum and quickly inject it into 2.5 mL of a mixed solution of 5% glucose and a certain concentration of PVA (external aqueous phase), vortex and mix to form a W/O/W type double emulsion, transfer the double emulsion to an evaporating dish, place it on a water bath at (37±2) degrees Celsius while introducing nitrogen to the liquid surface for 20 minutes, and obtain a light milky white suspension of AMK-MVLs.
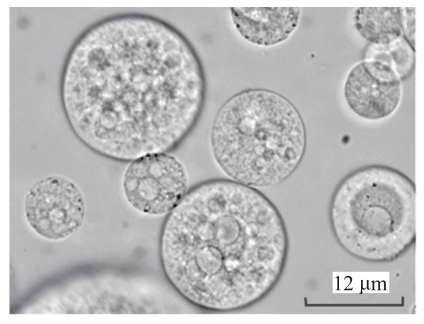
Figure 2 Particle morphology under optical microscope
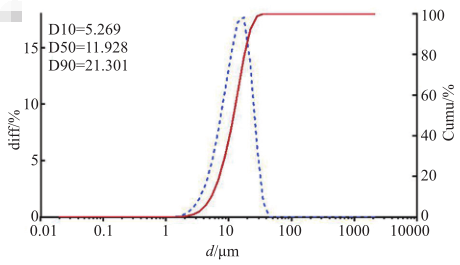
Figure 3 Particle size distribution
AMK-MVLs are round and smooth on the outside without adhesion, showing a typical non-concentric spherical structure with countless vesicles stacked inside; the average particle size is 11.93 μm, and the particle size distribution is uniform.
Jin241129M